■ Eduction
- Seoul National University (Agricultural chemistry, BS)
- University of Georgia (Biochemistry, PhD)
■ Research Area
1. Plant biochemistry and molecular biology
2. Transcription control mechanism for stress responses
3. Epigenetics on stress memory in plants
■ Recent Publications
1. Choonkyun Jung, Jun Sung Seo, Sang Won Han, Yeon Jong Koo, Chung Ho Kim, Sang Ik Song, Baek Hie Nahm, Yang Do Choi, and Jong-Joo Cheong (2008) Overexpression of AtMYB44 enhances stomatal closure to confer abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology 146(2), 623-635.
2. Nguyen Hoai Nguyen, and Jong-Joo Cheong (2018) AtMYB44 interacts with TOPLESS-RELATED corepressors to suppress Protein Phosphatase 2C gene transcription. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 507(1-4), 437-442.
3. Nguyen Hoai Nguyen, Choonkyun Jung, and Jong-Joo Cheong (2019) Chromatin remodeling for the transcription of type 2C protein phosphatase genes in response to salt stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 141, 325-331.
■ Research highlight
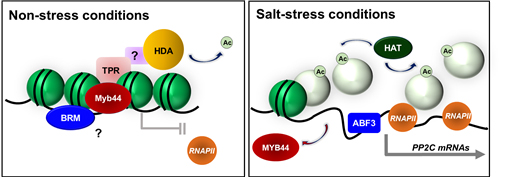
A working model for the regulation of PP2C gene expression. Under normal conditions, AtMYB44 (MYB44) interacts with a TOPLESS-RELATED corepressor (TPR), which recruits histone deacetylase (HDA) to suppress the PP2C gene transcription. Chromatin remodeler BRM complex contributes to the repression of PP2C gene transcription. Under salt stress conditions, PP2C gene promoters release the AtMYB44 repressors. Nucleosomes are acetylated (Ac) by histone acetyltransferases (HAT) and evicted. Activators (ABF3) bind to the open promoter region, and RNA polymerases (RNAPII) start gene transcription.

