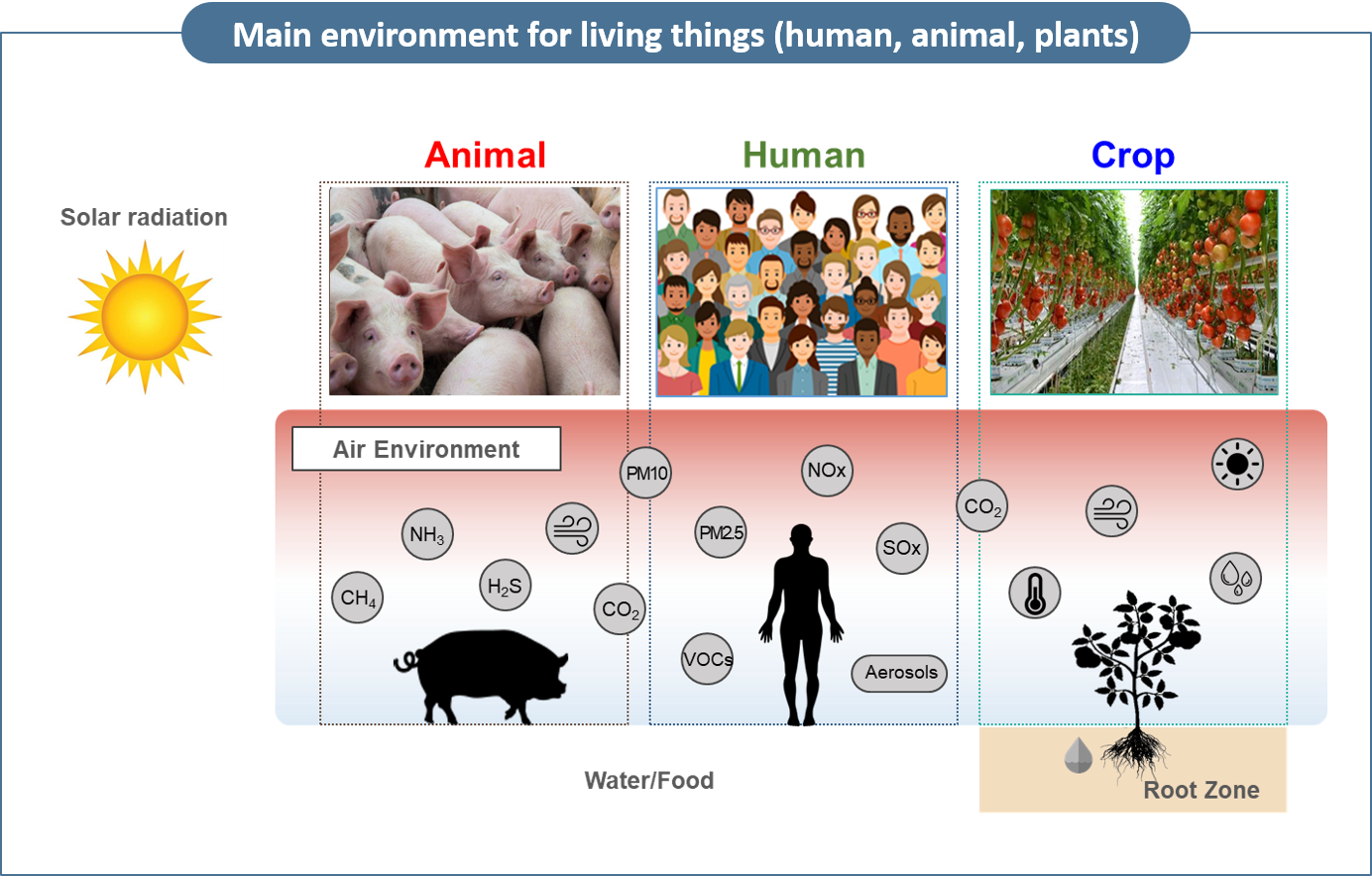
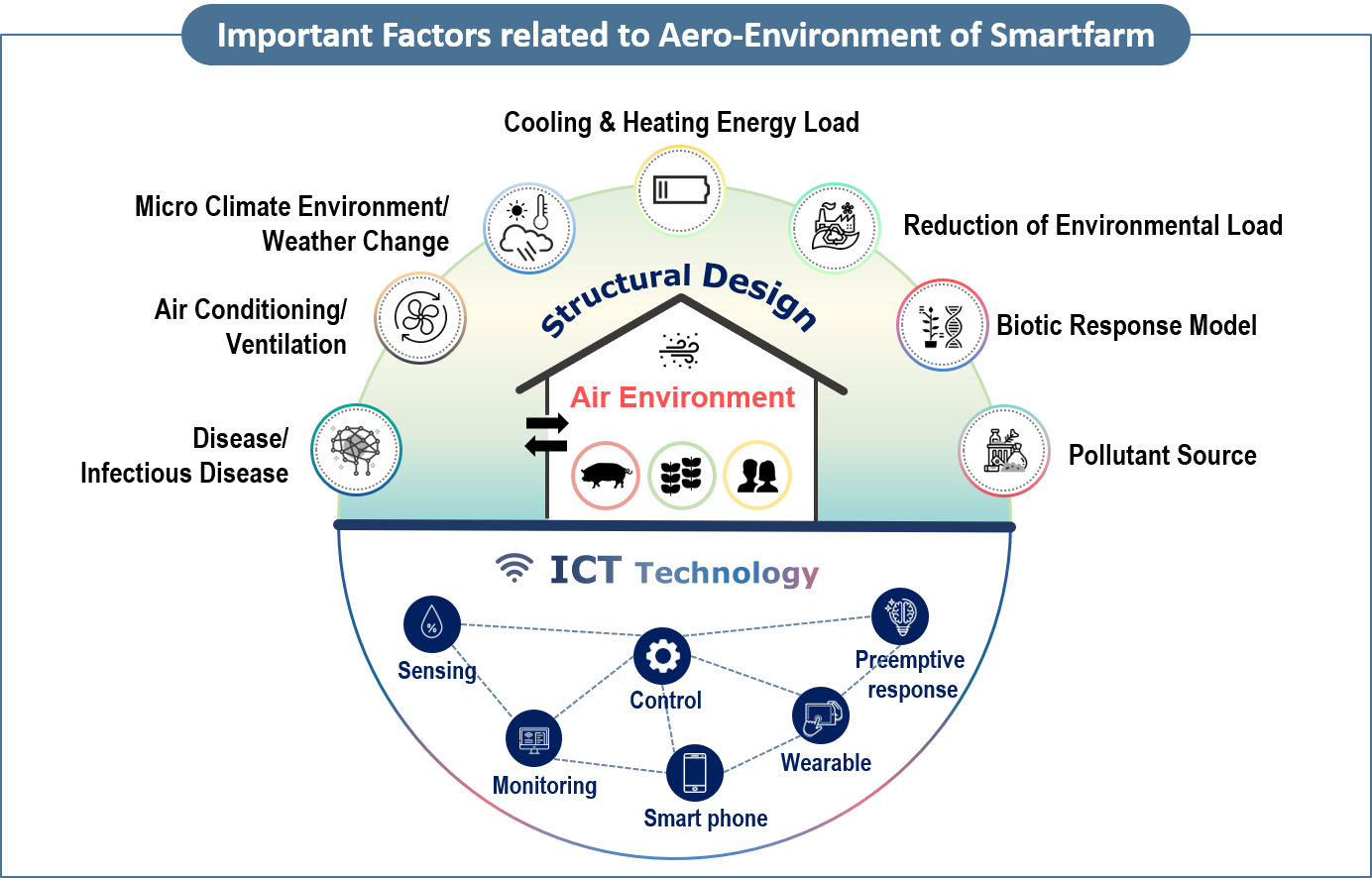
The world today is geared towards caring the environment. Renewable energies are now being explored to end mankind's dependence on petroleum fuels which continues to harm the environment. Biodiesel oil from biomass is very promising. Other sources such as solar, water and wind power to generate energy is a very significant research to undertake. Air pollution from aerosols, gases and odors from various sources is also an environmental concern. Air pollution significantly affects not only the human environment but also the growth of plants and animals. To mitigate problems caused by such pollution, qualitative and quantitative analysis of the pollutants considering the unstable weather conditions as well as their diffusion mechanisms are necessary.
In the design HVAC system of large size facilities especially in greenhouses, livestock houses, storage houses, etc., the analysis of air flow characteristics inside the facilities is very important to ensure environmental stability and uniformity. An aerodynamic approach using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is one of the most promising tools which can be utilized in the conduct of researches mentioned above. Computational fluid dynamics is a computational technology that enables the study of things that flow. This tool uses computers and numerical techniques to solve problems involving the movement of fluids. Using CFD, a computational model that represents a system or device can be built and by applying fluid flow physics and chemistry to this virtual prototype, a prediction of the fluid dynamics and the related physical phenomena can be determined.
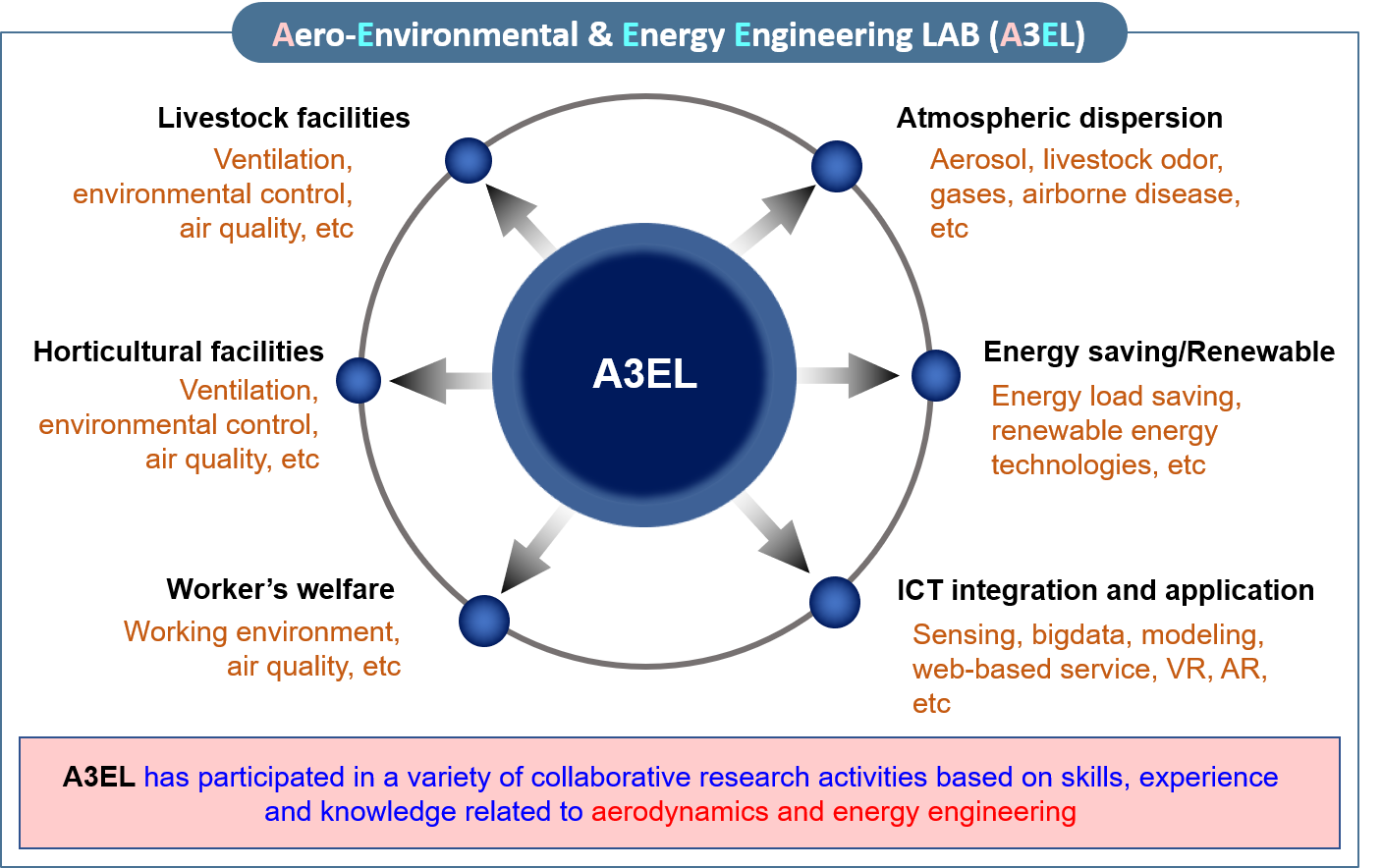
Our laboratory is focused on conducting simulation analysis in tandem with field experiments. At present, studies focusing on the air pollution, ventilation on agricultural facilities (greenhouse, livestock house, storehouse, etc.), renewable energy (wind and biofuel) are being conducted. Field measurements utilizing the ultramodern instruments and satellite data which employ theoretical analysis with numerical and experimental techniques are in progress. Likewise, three dimensional computation fluid dynamics (3D-CFD) models were continuously designed and developed. Wind tunnel as well as PIV experiments for air flow visualization and quantification are also utilized to establish the reliability and accuracy of the CFD models. The use of other equally important software tools, such as FLUENT, TRNSYS, GAMBIT, ENSIGHT, etc. also delivers a more systematic, efficient and economical approach in the modeling researches mentioned.